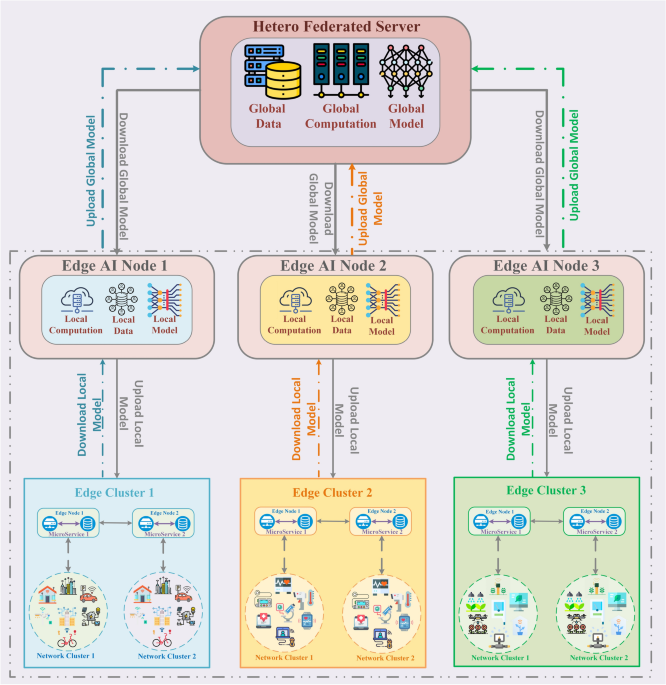
Introduction The rapid increase of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and transportable technology in recent years has led to an exponential increase in application data generation1. According to a Cisco report2, around 2.32 zeta bytes of data are produced daily at the network edge of 2023. This enormous volume of edge data has driven the

Unraveling the AI Revolution | Conn Kavanaugh – JDSupra
Decoding the potential, applications, and legal considerations of artificial intelligence in 2024 and beyond.
The rapid rise of artificial intelligence (“AI”) is reshaping industries, transforming economies, and presenting profound legal and ethical challenges. In 2024, AI technologies are no longer confined to the realm of science fiction but are actively woven into the fabric of our daily lives—from the recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms to complex predictive models in healthcare and autonomous vehicles. As AI continues its ascent, understanding its potential, its applications, and the legal landscape it influences is essential for businesses, lawyers, lawmakers, and society at large.
Understanding the Potential of AI
Artificial intelligence encompasses a range of technologies designed to simulate human-like decision-making, learning, and problem-solving abilities. These technologies range from machine learning, where systems improve through experience, to natural language processing, which enables machines to understand and respond to human language. Other critical components include computer vision, robotics, and deep learning, which have propelled the advancement of autonomous systems and complex data analysis.
The potential of AI is vast. For instance, in healthcare, AI-powered diagnostics have significantly increased the accuracy and speed of disease detection. In the legal field, AI tools assist lawyers by conducting document analysis, streamlining case research, and even predicting case outcomes based on historical data. In finance, AI-driven algorithms enhance fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service. The list of potential applications is almost endless, and while these advancements offer remarkable benefits, they also introduce new layers of risk and responsibility.
Applications of AI Across Industries
AI’s ability to automate tasks and analyze vast amounts of data is having transformative effects across numerous sectors. In manufacturing, AI-enhanced robotics and predictive maintenance software optimize production lines and extend equipment lifespan, boosting productivity and reducing downtime. Retail and e-commerce companies leverage AI to personalize customer experiences, manage inventory, and refine targeted marketing strategies. Meanwhile, government agencies are beginning to deploy AI for purposes ranging from data-driven policymaking to automated processing of public records.
One of the most profound areas of AI application is in autonomous vehicles. Self-driving cars use AI to interpret real-time data from their surroundings, navigating roads, and making split-second decisions. In 2024, while fully autonomous vehicles are not yet a common sight on public roads, the industry is advancing rapidly, posing significant legal questions regarding liability, regulation, and safety.
In addition to sector-specific applications, generative AI, which creates new content based on user inputs, has exploded in popularity. This subset of AI powers chatbots, virtual assistants, and creative tools that can produce text, images, and audio. However, these applications also bring concerns about copyright, content authenticity, and data privacy, raising new issues for the legal system to address.
Legal Considerations Surrounding AI
The accelerating deployment of AI raises significant legal and regulatory challenges that require careful consideration. As AI technologies become more integrated into daily operations and decision-making processes, the legal system must evolve to address new forms of risk, responsibility, and accountability. Here are some of the key legal considerations related to AI:
- Data Privacy and Security: AI systems rely on vast amounts of data, much of which is personal and sensitive. The use of such data, particularly in the context of personalized services or predictive analytics, raises concerns regarding privacy and consent. Legislations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States have laid the groundwork for data protection in the AI era. However, as AI grows more sophisticated, so must these regulatory frameworks to ensure robust protections against unauthorized data collection, processing, and storage.
- Intellectual Property Rights: Generative AI tools that create content pose novel challenges to traditional intellectual property (IP) frameworks. Who owns the copyright to AI-generated content? This question, yet unanswered in most jurisdictions, has implications for creators, developers, and end-users alike. Determining authorship and ownership of AI-created works requires legal reforms that can balance innovation with protecting the rights of human creators.
- Liability and Accountability: The use of autonomous AI systems, particularly in critical sectors like healthcare, finance, and transportation, brings unique liability concerns. In cases where an AI system’s decision leads to harm, identifying responsibility can be challenging. Should liability lie with the developers, the operators, or the AI system itself? While legal principles such as strict liability may apply, there is a growing call for regulatory guidance to clarify accountability in cases involving AI failures or malfunctions.
- Bias and Discrimination: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate or amplify biases present in their training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. Bias in AI has been a focal point in sectors like hiring, criminal justice, and lending, where biased AI systems can have significant adverse impacts on individuals and communities. Legal frameworks must evolve to ensure AI applications comply with anti-discrimination laws and to promote fairness in algorithmic decision-making.
- Ethics and Governance: As AI systems become more capable, ethical questions around human autonomy, transparency, and AI’s impact on employment and societal norms become unavoidable. Establishing robust governance frameworks and ethical guidelines can help mitigate the risks associated with AI, balancing technological progress with societal well-being. Lawmakers are increasingly interested in building AI governance frameworks that prioritize transparency, accountability, and public trust.
Moving Forward: Legal Preparedness in the AI Age
AI is a double-edged sword, promising immense benefits while simultaneously posing significant risks. As AI continues to evolve, so must our legal systems and regulatory frameworks to address these complexities. Lawyers and lawmakers must actively engage with technology experts to understand the underlying mechanisms of AI, its potential impacts, and the risks it entails.
Future regulations will likely focus on establishing standards for AI transparency, accountability, and fairness and ensuring that AI operates within ethical and legal bounds. However, achieving this balance requires a collaborative approach—bringing together legal minds, technologists, and policymakers to craft laws that can foster innovation while protecting society from the unforeseen challenges of the AI age.